In industrial plants—whether in manufacturing, energy, oil & gas, or chemical processing—machinery, pipelines, electrical panels, and valves must be constantly monitored. Routine inspection and maintenance are critical to ensure equipment is functioning correctly, avoid costly downtime, and extend asset life. Traditionally, these tasks have relied heavily on human labor. However, this approach is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to errors or oversights, especially in harsh or complex environments.
1. Challenges of Manual Inspection
Human-led inspections, while common, present several significant limitations:
- Time and labor intensive: Trained technicians are required to physically move through large facilities to inspect equipment—often taking hours or days.
- Safety concerns: Many industrial environments involve dangerous or hard-to-reach areas, such as high-temperature machinery, pressurized systems, or confined spaces. Sending humans into these areas exposes them to unnecessary risk.
- Inconsistencies and errors: Fatigue, distraction, or limited access can cause key details to be overlooked. Even with checklists, manual inspection results may vary between operators.
Worse still, if a developing issue is missed during inspection, it can lead to unplanned downtime, costly repairs, or even system-wide failures. This is where robotic inspection using quadruped robots, often called “robot dogs,” offers a breakthrough.

2. Why Use Robot Dogs for Preventative Maintenance?
Quadruped robots are four-legged machines designed for agile mobility and advanced perception. Their ability to navigate challenging terrain, avoid obstacles, and carry various sensors makes them ideally suited for industrial inspection. When used for preventative maintenance, robot dogs help detect problems before they escalate—allowing for proactive rather than reactive plant management.
Here’s how they add value:
- Improved safety: Robot dogs can access hazardous or high-risk areas without putting human workers in danger.
- Accuracy and consistency: With onboard sensors and automation, these robots deliver repeatable, accurate data—reducing human error.
- High frequency, low cost: Robot dogs can patrol daily or multiple times a day without fatigue. This increases inspection frequency and reliability while lowering long-term labor costs.
- Freeing up human resources: Skilled technicians can focus on repairs, planning, and decision-making rather than routine data collection.

3. What Can Robot Dogs Inspect?
Depending on the plant’s needs, robot dogs can be equipped with a tailored mix of sensors to gather precise, real-time data. Commonly used sensors include:
-
- Cameras (visual and infrared): Used for detecting visual anomalies such as corrosion, leaks, rust, or damaged insulation. Infrared cameras help detect overheating components or electrical faults.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Generates 3D maps and point clouds of environments. Used to track changes in equipment position or detect deformations, blockages, or misalignments over time.
- Thermal imaging: Ideal for identifying overheating equipment, motors, or electrical panels that could indicate underlying issues.
- Audio sensors: Help detect unusual sounds, such as irregular motor vibration, hissing from leaks, or pipe resonance—often early indicators of malfunction.
- Gas sensors: Detect leaks or abnormal concentrations of gases like methane, carbon monoxide, or volatile organic compounds, critical for chemical and energy plants.
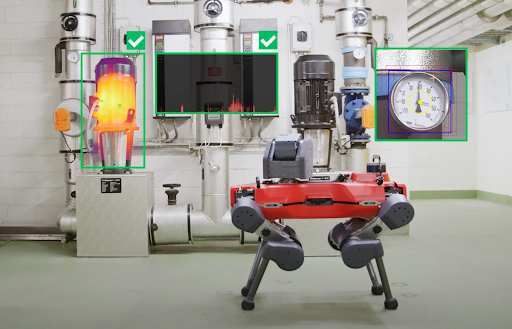
Figure 3: Thermal, audio and visual inspection in industrial plant using sensors
4. Data Management and Analysis
All sensor data collected by the robot dog is transmitted to a centralized software platform, where it is:
- Stored in the cloud or local servers
- Visualized via dashboards showing past, present, and trend-based predictions
- Analyzed using AI or human review to generate alerts and inspection reports
Over time, this data builds up a digital history of equipment condition, enabling predictive maintenance and even AI-driven diagnostics.
5. Looking Forward
As robot dogs become more affordable and robust, they are rapidly being adopted across industries for routine inspections. By combining mobility, autonomy, and rich data capture, these intelligent machines help plants reduce risks, save time, and stay ahead of costly breakdowns.
In the future, robot dogs may also perform simple physical tasks—such as pushing buttons, tightening valves, or manipulating tools—further extending their role from monitoring to light maintenance assistance.








Leave a Reply