Industrial robots are increasingly playing a crucial role in modern manufacturing plants, contributing to enhanced efficiency, quality, and competitiveness for businesses. This article will present the concept of industrial robots, common types of robots, their applications in manufacturing, and the benefits they bring to the production process.

1. Concept of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are automated, programmable machines designed to perform specific production tasks in industrial environments. They typically have the ability to move along two or more axes and are equipped with sensors, controllers, and actuators to carry out precise, repetitive operations. These robots can replace or assist humans in tasks that are heavy, dangerous, or require high precision. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), an industrial robot is defined as “an automatically controlled, reprogrammable machine capable of movement along two or more axes, used in industrial applications.” They can perform tasks such as welding, painting, assembly, transportation, and product quality inspection.
2. Common types of robots in industry
Industrial robots are designed in various forms to meet different production needs. Below are some common types:
Articulated Robot: Structured like a human arm with flexible joints, suitable for welding, painting, and assembly.

CARA Robot: Flexible in the X and Y axes but rigid in the Z axis, commonly used in assembly and packaging.
Delta Robot: Known for high speed and precision, often applied in packaging and product sorting.
Collaborative Robot (Cobot): Designed to work safely alongside humans, assisting in tasks like assembly and quality inspection.
Cartesian Robot: Moves along the X, Y, and Z axes, ideal for 3D printing, laser cutting, and machining.
Quadruped Robot: Designed to move on four legs, providing stability and flexibility in complex terrains, often used for inspection, monitoring, and transportation in hazardous or hard-to-reach industrial environments.

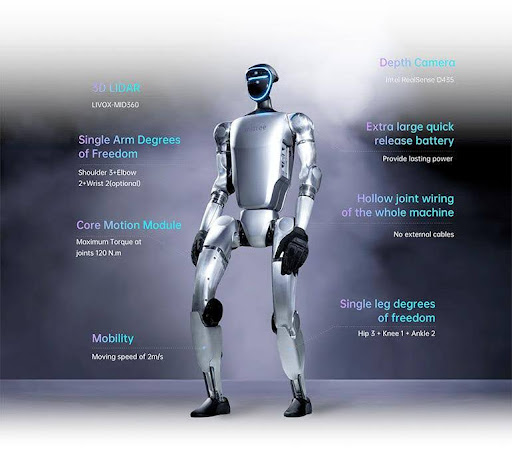
Humanoid Robot: Shaped and functions like a human, typically used for tasks requiring high interaction with people, such as customer support or performing complex production tasks.
AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot): A self-navigating mobile robot that moves autonomously in the workspace without fixed paths, commonly used for transporting goods, materials, or tools in factories.
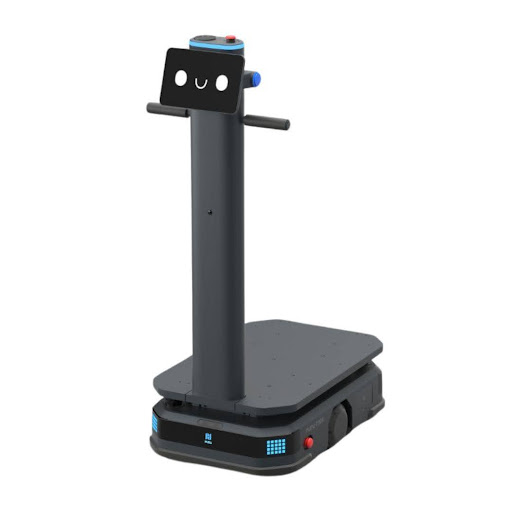

AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle): A mobile robot that follows fixed paths (such as magnetic strips or lasers), often used for transporting goods in factories to optimize logistics and reduce manual labor.
3. Applications of Industrial Robots in Manufacturing Plants
Industrial robots are widely applied across various production sectors, delivering optimal efficiency and enhancing business competitiveness. Below are some key and detailed applications of industrial robots in manufacturing plants:

Welding: Robots perform precise welds in industries such as automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace. Common welding techniques include arc welding, spot welding, as well as advanced methods like laser welding, plasma welding, and friction stir welding (FSW), which are particularly useful in medical device manufacturing and complex structures.

Painting: Robots ensure even paint layers and reduce material waste in the production of cars, household appliances, and industrial equipment. They also handle complex painting techniques such as electrostatic painting, UV painting, and anti-corrosion coatings, improving product durability and quality.
Assembly: Robots increase speed and precision in assembling electronic components, mechanical parts, engines, medical devices, and household appliances. They can handle complex assembly processes, ensuring consistency and high quality.
Packaging and Palletizing: Robots automate the processes of packaging, stacking, sealing, labeling, and inspecting packaging quality, saving time and labor. This application is particularly effective in the food, beverage, and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industries.
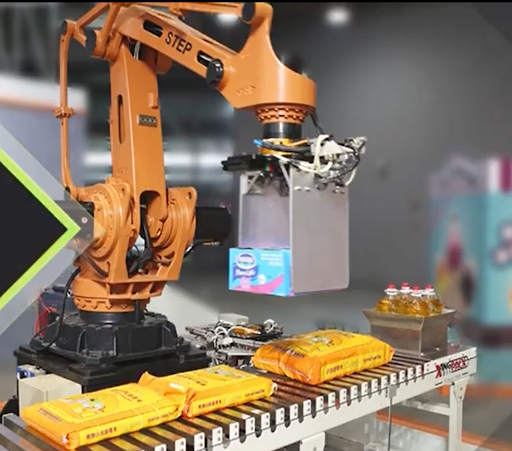

Quality Inspection: Using sensors, cameras, computer vision, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, robots detect even the smallest defects in products, ensuring high quality in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Internal Transportation: Autonomous robots such as AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) move goods, optimizing logistics within the factory. AMRs stand out for their ability to navigate flexibly without fixed paths.
Machining: Robots perform machining tasks such as cutting, grinding, polishing, and drilling with high precision, suitable for mechanical engineering, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Material Handling: Robots move, sort, and store heavy or hazardous materials, reducing the risk of workplace accidents and improving material management efficiency.
Maintenance and Repair: Robots carry out regular maintenance, equipment inspections, and minor repairs, helping to reduce downtime and maintain continuous operations.
Research and Development: In laboratories, robots are used to conduct experiments, test new products, and develop technologies, accelerating innovation and creativity.
The application of industrial robots not only boosts productivity, reduces costs, and improves product quality but also enhances workplace safety and environmental protection, contributing to the development of smart and sustainable factories.
4. Benefits of Applying Industrial Robots in Manufacturing Plants
The use of industrial robots brings numerous practical benefits, including:
Increased Productivity: Operating continuously 24/7, meeting high production demands at fast speeds.
Improved Quality: Ensuring precision and uniformity, minimizing defects in products.
Reduced Labor Costs: Replacing manual labor, saving on workforce and training expenses.
Enhanced Safety: Performing dangerous tasks, protecting workers’ health.
Flexibility: Easily programmable to adapt to different production tasks.
Material Savings: Reducing waste through high precision, contributing to environmental protection.
Industrial robots are not just automation tools but also a key to helping manufacturing plants optimize processes and enhance competitiveness in the Industry 4.0 era. For further information on this technology, you can refer to specialized resources or contact industrial robot solution providers.








Leave a Reply